Radiology and Lab Services
At our vet clinic, we are proud to offer digital radiography as a diagnostic tool for our patients. Digital radiography, also known as digital x-ray, is a modern and efficient way to capture and analyze x-ray images.
If you have any questions about digital radiography or would like to schedule an appointment for your pet, please don't hesitate to contact us. We would be happy to help.
In house Lab Services
Advanced Veterinary Care has in house laboratory services available
Appointment Based
These services are performed through appointment based system.
Digital Radiographs (x-rays)
Using x-ray technology, images of a certain body cavity are acquired. Typically, in our service, this test is done to screen for cancers, heart disease/heart failure, respiratory disease. We may acquire abdominal x-rays on occasion for certain conditions such as bladder stones, but typically will using an ultrasound for the abdomen.
CT scan
(CT or CAT scan) is using the same technology as digital x-rays, however the images are acquired in transverse and therefore more information about imaged area is acquired. Certain disease process such as metastatic disease (cancer) is detected earlier on a CT scan compared to chest x-rays. The time required for a CT scan is slightly longer compared to x-rays but typically less than ½ hour. In most patients this test will require general anesthesia.

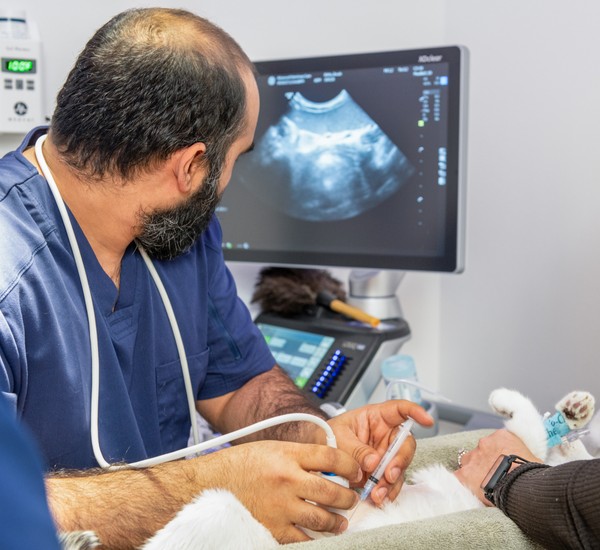
Abdominal Ultrasound
Ultrasound waves are used to acquire the imaging without any radiation. Anesthesia is not required, however some patients may need sedation to facilitate the test. For medium/big dogs, some abdominal organs (i.e liver, adrenal glands) are not visualized well and a CT may be more diagnostic.
Other diagnostics
Ultrasound guided needle aspirates for cytology: as part of diagnostic imaging, we may encounter abnormalities such tumors, lymph node (or organ such as liver or spleen) enlargement, or other abnormalities that are suspicious for underlying insidious disease that warrants examination of cells under a microscope.
Risks
Risks of imaging tests are relatively low, however there is risk involved with anesthesia or sedation. General blood work should be done within two to four weeks before general anesthesia. If a needle aspirate is attained during imaging tests, the biggest risk for this procedure is risk of bleeding (especially with liver or spleen aspirates), typically this risk is low if bloodwork is normal. Needle aspirates also carry a risk of a non-diagnostic sample, where a biopsy may be required in the future.



